On Country
Distance of a Projectile
An Introduction to Vectors
Definitions
A vector is an object with magnitude and direction (velocity, force, acceleration, etc). A scalar is an object with just magnitude (temperature, pressure, age, length). A vector, denoted ➔v or v, has no initial point and is often best thought of as at the origin.
http://web.eecs.umich.edu/~sugih/courses/eecs487/common/notes/VM.pdf
Vector projection
The vector projection of 1 vector over another vector is the length of the shadow of the given vector over another vector. It is obtained by multiplying the magnitude of the given vectors with the cosecant of the angle between the two vectors. The resultant of a vector projection formula is a scalar value.
https://www.cuemath.com/geometry/projection-vector/
Projection vector formula
The projection of vector a➔ (in the diagram) on vector b➔ is equal to the product of vector a and b, divided by the magnitude (length) of vector b, giving a scalar value, (a x b)/b.
Activity
Understand the Structure of Plant Tissues:
MATERIALS
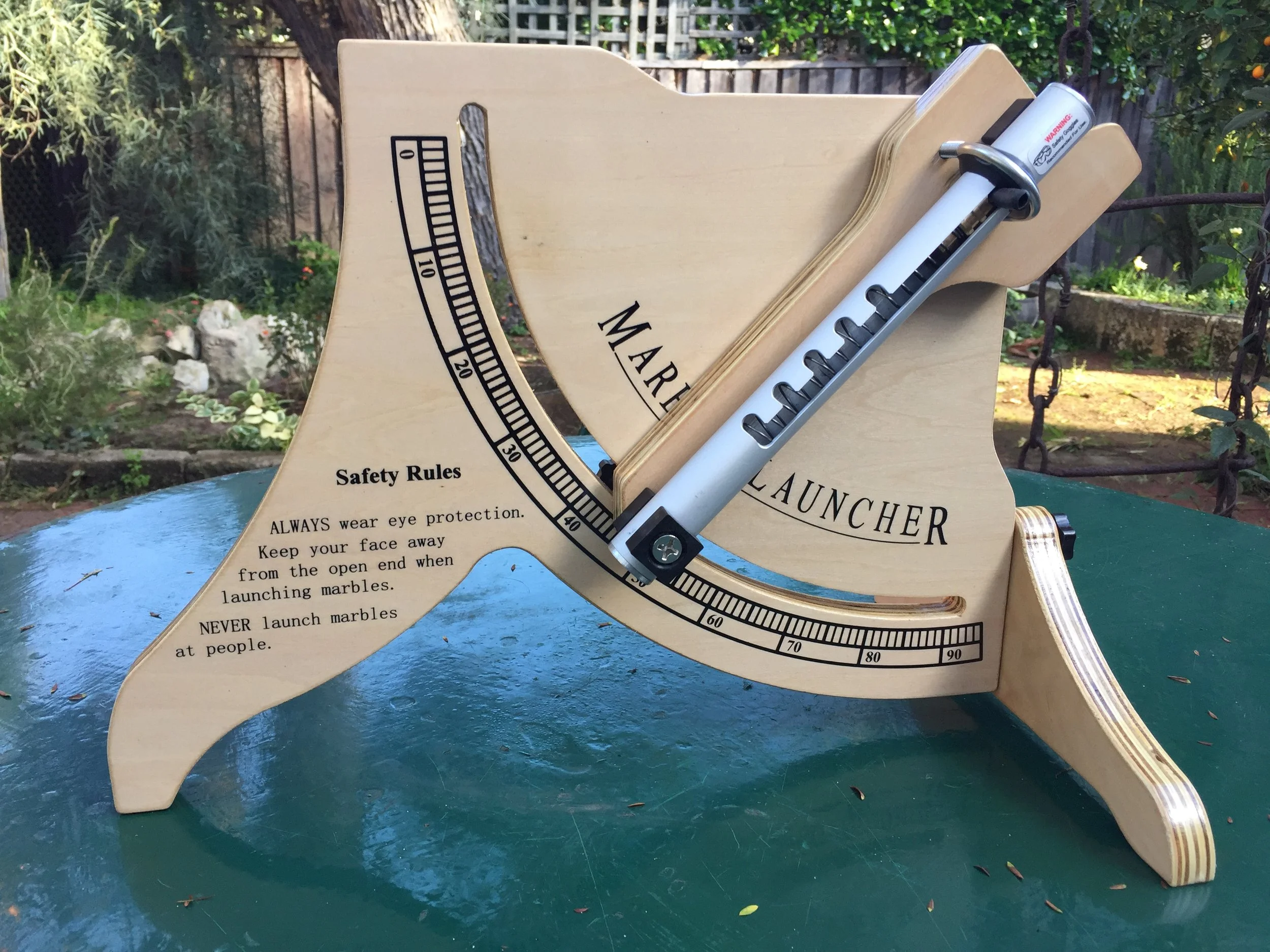
1. Using a marble launcher (See Equipment in TOOLBOX)
• marble launcher
• marbles
• measuring tape
• notebook & pencil
2. Using a foam javelin (See Equipment in TOOLBOX)
• foam javelin
• protractor
• measuring tape
• notebook & pencil
METHOD
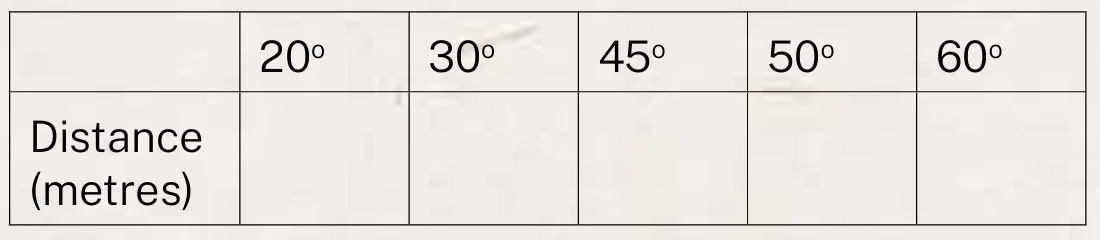
1. Students predict at which angle the marble (or javelin) will travel the furthermost.
2. Using the launcher (which should project with a constant force), each student projects a marble at angles of 20o, 45o, and 60o (or others in addition).
3. Measure the distance travelled by the marble each time, and record.
4. Average the results at each angle and enter a Class Table.
5. Using the javelin, have the student launcher project the javelin at different angles (keeping the force constant).
6. Using a protractor, measure the angle at each throw made by the student’s body and the straight arm at launching.
7. Measure the distance travelled by the javelin each time, and record.
8. Average the results at each angle and enter a Class Table.
9. RECORD results in a Table, labelled with the method chosen.
• Draw a diagram similar to that shown in the Figure, measuring the angle and distance along the x-axis, with each angle measured.
• Develop a scale that associates an angle with a distance.
Angle of projection. From Cuemath
Marble launcher